A balance sheet, also known as a "statement of financial position", reveals a company's assets, liabilities and owners' equity (net worth). The balance sheet, together with the income statement and cash flow statement, make up the cornerstone of any company's financial statements. If you are a shareholder of a company, it is important that you understand how the balance sheet is structured, how to analyze it and how to read it. (To learn more, check out An Introduction To The Balance Sheet from Investopedia Video.)How the Balance Sheet Works
The balance sheet is divided into two parts that, based on the following equation, must equal each other, or balance each other out. The main formula behind balance sheets is:This means that assets, or the means used to operate the company, are balanced by a company's financial obligations along with the equity investment brought into the company and its retained earnings.
Assets are what a company uses to operate its business, while its liabilities and equity are two sources that support these assets. Owners' equity, referred to as shareholders' equity in a publicly traded company, is the amount of money initially invested into the company plus any retained earnings, and it represents a source of funding for the business.
It is important to note that a balance sheet is a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a single point in time.
Know the Types of Assets
* Current Assets
Current assets have a life span of one year or less, meaning they can be converted easily into cash. Such assets classes include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and inventory. Cash, the most fundamental of current assets, also includes non-restricted bank accounts and checks. Cash equivalents are very safe assets that can be readily converted into cash; U.S. Treasuries are one such example. Accounts receivables consist of the short-term obligations owed to the company by its clients. Companies often sell products or services to customers on credit; these obligations are held in the current assets account until they are paid off by the clients. Lastly, inventory represents the raw materials, work-in-progress goods and the company’s finished goods. Depending on the company, the exact makeup of the inventory account will differ. For example, a manufacturing firm will carry a large amount of raw materials, while a retail firm caries none. The makeup of a retailer's inventory typically consists of goods purchased from manufacturers and wholesalers.
* Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets are assets that are not turned into cash easily, are expected to be turned into cash within a year and/or have a life-span of more than a year. They can refer to tangible assets such as machinery, computers, buildings and land. Non-current assets also can be intangible assets, such as goodwill, patents or copyright. While these assets are not physical in nature, they are often the resources that can make or break a company - the value of a brand name, for instance, should not be underestimated.
Depreciation is calculated and deducted from most of these assets, which represents the economic cost of the asset over its useful life.
Learn the Different Liabilities
On the other side of the balance sheet are the liabilities. These are the financial obligations a company owes to outside parties. Like assets, they can be both current and long-term. Long-term liabilities are debts and other non-debt financial obligations, which are due after a period of at least one year from the date of the balance sheet. Current liabilities are the company’s liabilities which will come due, or must be paid, within one year. This is includes both shorter term borrowings, such as accounts payables, along with the current portion of longer term borrowing, such as the latest interest payment on a 10-year loan.
Shareholders' Equity
Shareholders' equity is the initial amount of money invested into a business. If, at the end of the fiscal year, a company decides to reinvest its net earnings into the company (after taxes), these retained earnings will be transferred from the income statement onto the balance sheet into the shareholder’s equity account. This account represents a company's total net worth. In order for the balance sheet to balance, total assets on one side have to equal total liabilities plus shareholders' equity on the other.
Read the Balance Sheet
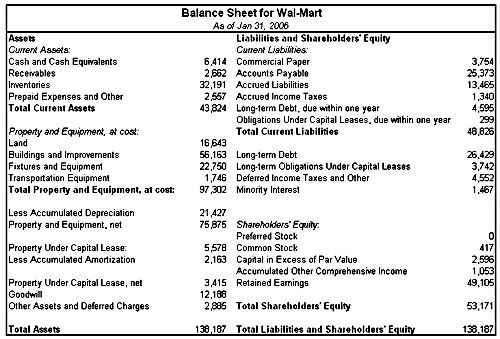
Below is an example of a balance sheet:As you can see from the balance sheet above, it is broken into two sides. Assets are on the left side and the right side contains the company’s liabilities and shareholders’ equity. It is also clear that this balance sheet is in balance where the value of the assets equals the combined value of the liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
Another interesting aspect of the balance sheet is how it is organized. The assets and liabilities sections of the balance sheet are organized by how current the account is. So for the asset side, the accounts are classified typically from most liquid to least liquid. For the liabilities side, the accounts are organized from short to long-term borrowings and other obligations.
Analyze the Balance Sheet With Ratios
With a greater understanding of the balance sheet and how it is constructed, we can look now at some techniques used to analyze the information contained within the balance sheet. The main way this is done is through financial ratio analysis.
Financial ratio analysis uses formulas to gain insight into the company and its operations. For the balance sheet, using financial ratios (like the debt-to-equity ratio) can show you a better idea of the company’s financial condition along with its operational efficiency. It is important to note that some ratios will need information from more than one financial statement, such as from the balance sheet and the income statement.
The main types of ratios that use information from the balance sheet are financial strength ratios and activity ratios. Financial strength ratios, such as the working capital and debt-to-equity ratios, provide information on how well the company can meet its obligations and how they are leveraged. This can give investors an idea of how financially stable the company is and how the company finances itself. Activity ratios focus mainly on current accounts to show how well the company manages its operating cycle (which include receivables, inventory and payables). These ratios can provide insight into the company's operational efficiency.
There are a wide range of individual financial ratios that investors use to learn more about a company. (To learn more about ratios and how to use them, see our Ratio Tutorial.)
Conclusion
The balance sheet, along with the income and cash flow statements, is an important tool for investors to gain insight into a company and its operations. The balance sheet is a snapshot at a single point in time of the company’s accounts - covering its assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity. The purpose of the balance sheet is to give users an idea of the company’s financial position along with displaying what the company owns and owes. It is important that all investors know how to use, analyze and read this document.
(To learn more about reading financial statements, see What You Need To Know About Financial Statements, What Is A Cash Flow Statement? and Understanding The Income Statement.)
by Investopedia Staff
Investopedia.com believes that individuals can excel at managing their financial affairs. As such, we strive to provide free educational content and tools to empower individual investors, including thousands of original and objective articles and tutorials on a wide variety of financial topics.